Local folders can be assigned as network drives with drive letters via the command prompt on Microsoft Windows 11, 10, ... etc. Desktop and MS Server OS!The net use command is popular to assign your own computer to shared drives on a network as drive letters. Everyone knows the map network drive function , but very few people know that there is another command with which you can do the same in every folder on one of your local hard drives in order to access the folder directly via the drive letter ! Contents: 1.) ... Assign a drive letter to the local folder!
|
| (Image-1) Command to assign local folders as network drives with drive letters! |
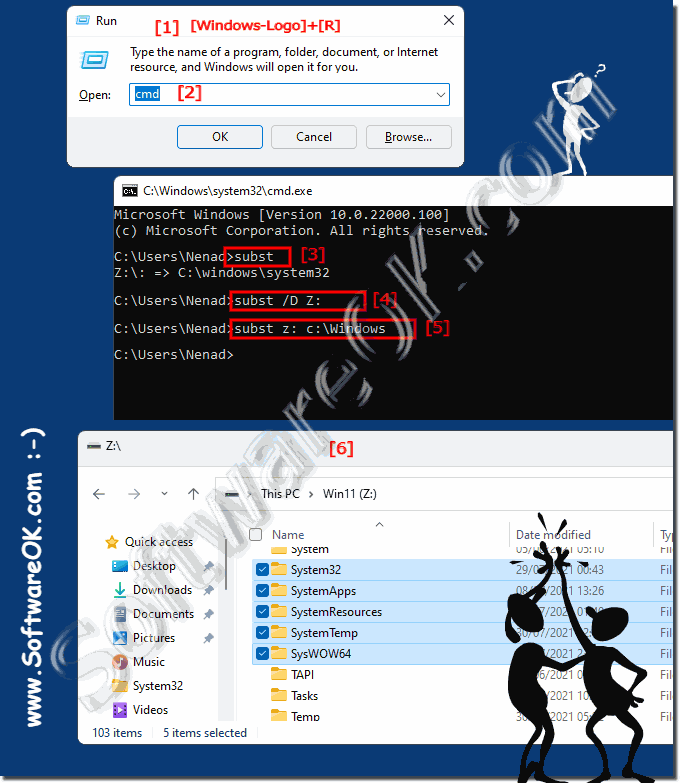 |
In this sense, the subst command can be used to replace the virtual drive letter with another drive letter on your computer.
2.) Release the drive letter again!
With the command:
subst /d z:
We can assign the to the folder and remove the access via P \ again!
( ... see Image-2 )
The functions of subst :
C:\Users\Nenad> subst /?
Assigns a drive label to a path.
SUBST [Drive1: [Drive2:] path]
SUBST Drive1: / D Drive1
: Name of the virtual drive that is
to be assigned to the path .
[Drive2:] Path Physical drive and physical path
to be assigned to the virtual drive.
/ D Removes the assignment for (virtual) drive1
.
SUBST without parameters shows the virtual drives created with SUBST.
| (Image-2) Remove the drive letter assignment from the local folder! |
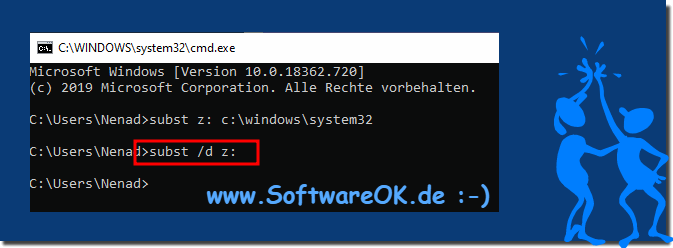 |
This command prompt trick can make it much easier to access a specific location via the command prompt and the folder will appear as a Windows drive next to all of your real hard drives.
3.) What should be considered when assigning drive letters, history!
You can only use free drive letters AZ!Drive letter mapping is the process of alphabetically mapping identifiers to the paths. In contrast to the concept of UNIX mount points, in which volumes are arbitrarily named and arranged in a single hierarchical namespace, drive letter assignment enables multiple namespaces at the highest level. Thus, drive letter assignment is a process of using letters to denote the roots of the "forest" that makes up the file system.
System drive:
The system/boot drive is usually assigned the letter “C:”. This has been a standard convention for Windows operating systems for many years. Changing the system drive letter can cause compatibility issues and software problems.
Reserved Drive Letters:
Some drive letters such as “A:” and “B:” are often reserved for historical reasons. Avoid assigning these letters to other drives as this may cause confusion or conflict.
Network drive mapping:
Network drives are often assigned letters such as “N:” or “Z:”. It's best practice to use consistent drive letters for network shares across your organization to ensure a consistent user experience.
USB drives and removable media:
USB drives and other removable media are often assigned the next available drive letter (e.g. "E:", "F:", etc.). Note that these letters may change as you use different devices. It can be helpful for users to label their drives.
Avoid using the same drive letter twice:
Use the built-in Windows Disk Management tool to assign or change drive letters. This ensures that the changes are made correctly and are reflected in the operating system.
If you change drive letters, ensure that backup and restore procedures are updated accordingly. Backups should contain the new drive letter assignments.
Document tasks:
Keep records of drive letter assignments, especially in a business or network environment. This documentation can help troubleshoot problems and support new users.
In summary, drive letter assignment should take into account historical conventions, established practices, and compatibility considerations to ensure a smooth and consistent user experience. Avoid arbitrary drive letter changes, especially for system and network drives, to avoid confusion and potential problems.
FAQ 72: Updated on: 10 October 2023 16:39
